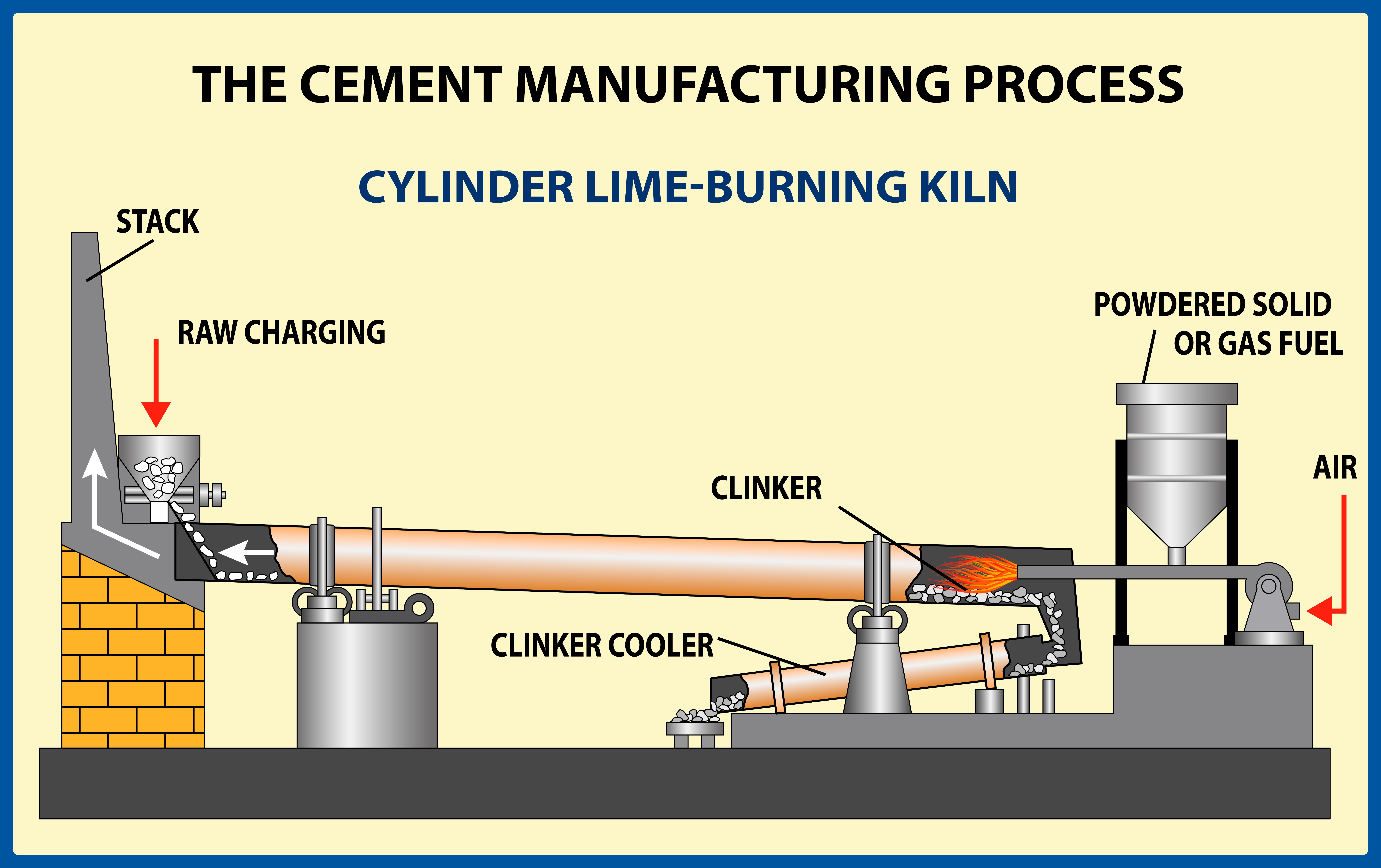
Alumino-silicate bricks, essential for the lining of kilns and other high-temperature equipment in the cement industry, are designed to endure extreme conditions and aggressive environments. These bricks, with alumina (Al₂O₃) content ranging from 30% to 85%, offer tailored solutions to meet the rigorous demands of cement production processes.
Composition and Classification
Low-Alumina Bricks (30-45% Al₂O₃)
- Al₂O₃ Content: 30-45%
- SiO₂ Content: 55-70%
- Application: Typically used in the cooler zones of cement kilns and other areas with lower thermal requirements.
Medium-Alumina Bricks (45-60% Al₂O₃)
- Al₂O₃ Content: 45-60%
- SiO₂ Content: 40-55%
- Application: Suitable for zones with moderate thermal and mechanical stress, such as transition zones in rotary kilns.
High-Alumina Bricks (60-85% Al₂O₃)
- Al₂O₃ Content: 60-85%
- SiO₂ Content: 15-40%
- Application: Ideal for high-temperature zones like the burning zones of rotary kilns, where excellent thermal resistance and stability are critical.
Physical and Thermal Properties
| Property | Low-Alumina Bricks | Medium-Alumina Bricks | High-Alumina Bricks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cold Crushing Strength (CCS) | 25-35 MPa | 35-55 MPa | 55-80 MPa |
| Refractoriness Under Load (RUL) | Up to 1300°C | Up to 1450°C | Up to 1600°C |
| Apparent Porosity | 20-26% | 18-23% | 15-20% |
| Thermal Conductivity | 1.0-1.3 W/m·K | 1.3-1.5 W/m·K | 1.5-1.7 W/m·K |
Advantages in Cement Production
- Thermal Stability: High alumina content ensures superior performance at elevated temperatures, crucial for different stages of cement production.
- Mechanical Strength: Enhanced CCS values provide resilience against mechanical wear and abrasion.
- Corrosion Resistance: Alumino-silicate bricks offer excellent resistance to alkali attacks and chemical erosion from cement clinker and other aggressive materials.
- Energy Efficiency: Optimal thermal conductivity minimizes heat loss, improving energy efficiency in cement kilns and other high-temperature applications.
Applications
- Rotary Kilns: High-alumina bricks are essential for the burning zone, ensuring durability under intense heat and corrosive conditions.
- Preheaters and Calciners: Medium-alumina bricks provide reliable performance in these areas, withstanding significant thermal cycling and mechanical stress.
- Coolers: Low-alumina bricks are used in cooler zones, offering effective insulation and resistance to lower temperature gradients.
By selecting the appropriate alumino-silicate bricks based on alumina content and specific property requirements, cement plants can optimise performance, extend refractory life, and enhance overall operational efficiency.